Key Authentication (Key Auth)
Overview
The Key Authentication (key-auth) policy enforces API security by requiring API consumers to include a valid API Key in their request headers. This mechanism ensures that only authorized users or applications can access the API.
How Key Authentication Works
- The API consumer must provide a valid API Key in the request headers.
- The API Gateway verifies the API Key before processing the request.
- If the API Key is missing or invalid, the request is denied with an authentication error.
When to Use Key Authentication
- To restrict API access to authorized clients.
- When an API consumer identification mechanism is needed.
- When combining multiple authentication methods (e.g., key-auth + JWT).
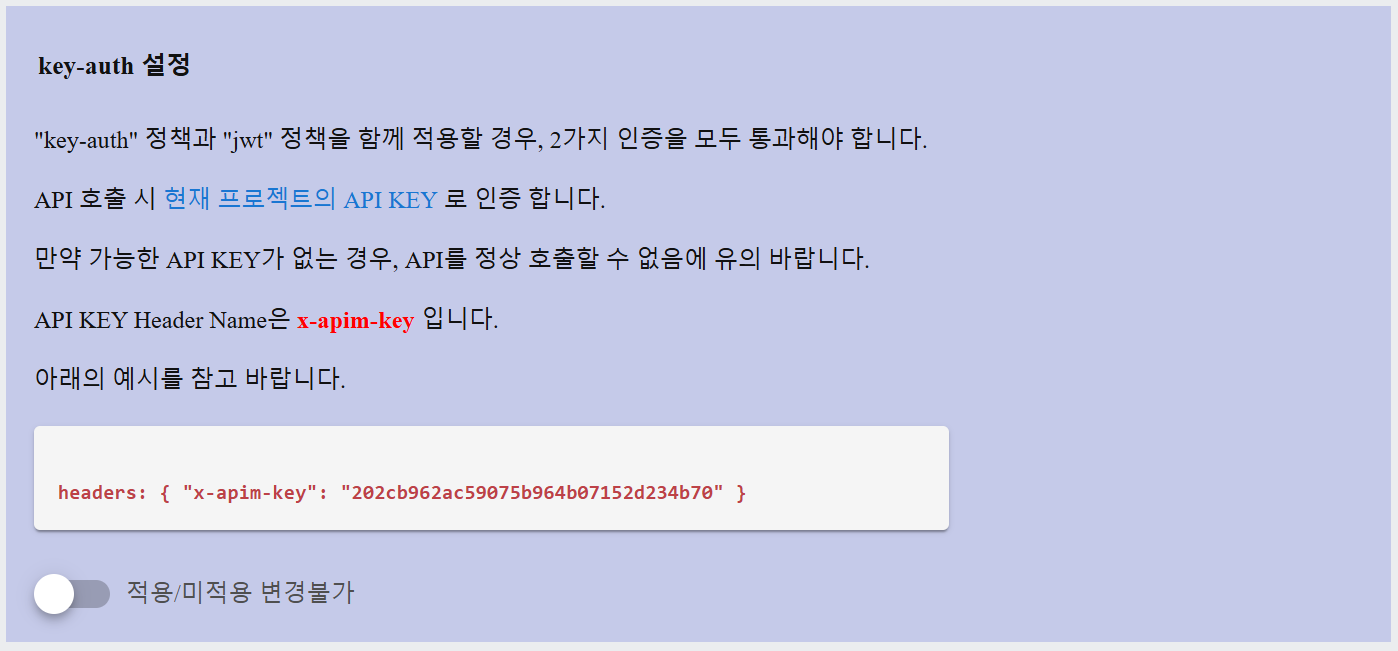
Note: If both key-auth and JWT authentication are enabled, both authentication methods must be passed for a successful request.
Configuration Details
Creating an API Key
Before applying the Key Authentication policy, an API Key must be generated. Follow these steps:
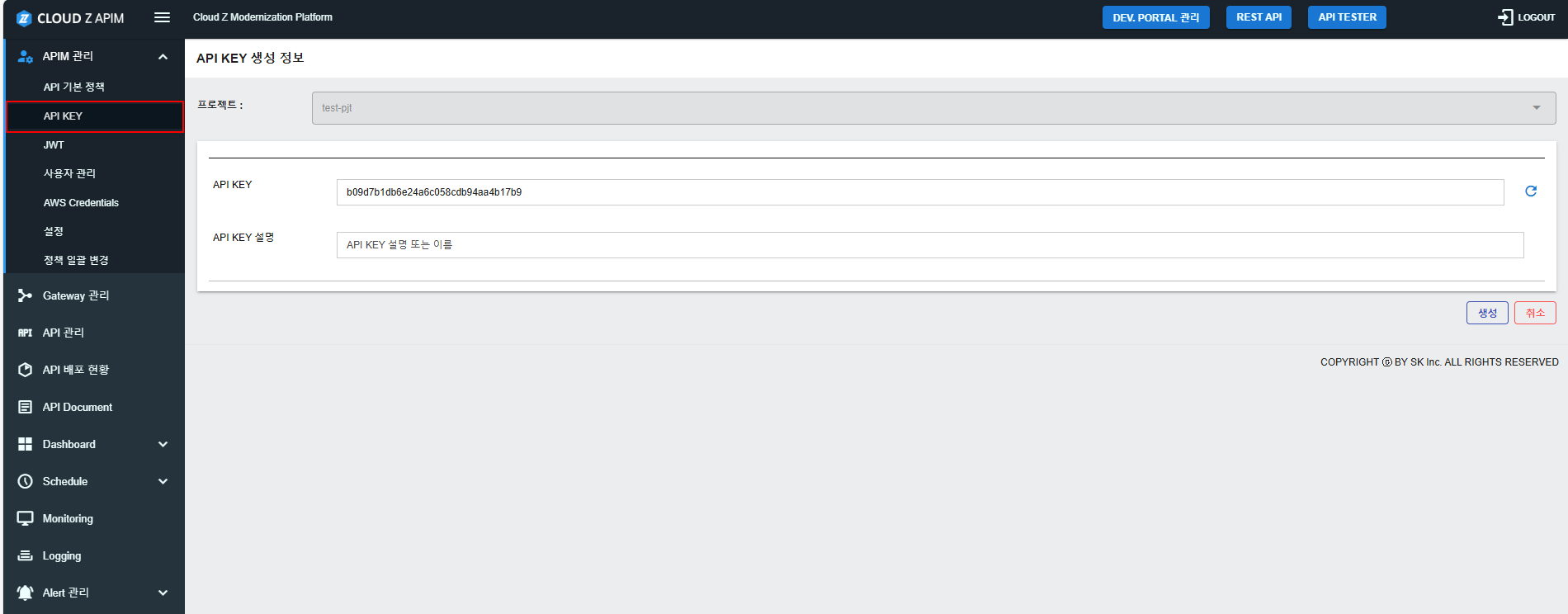
Step 1: Open the API Key Management Page- Navigate to the APIM Management menu in the APIM Console
- Select the project where you want to create an API Key.
- Click the Create API Key button.
- Enter a description for the API Key (e.g., "Key for Mobile App Access").
- The system will automatically generate a unique API Key.
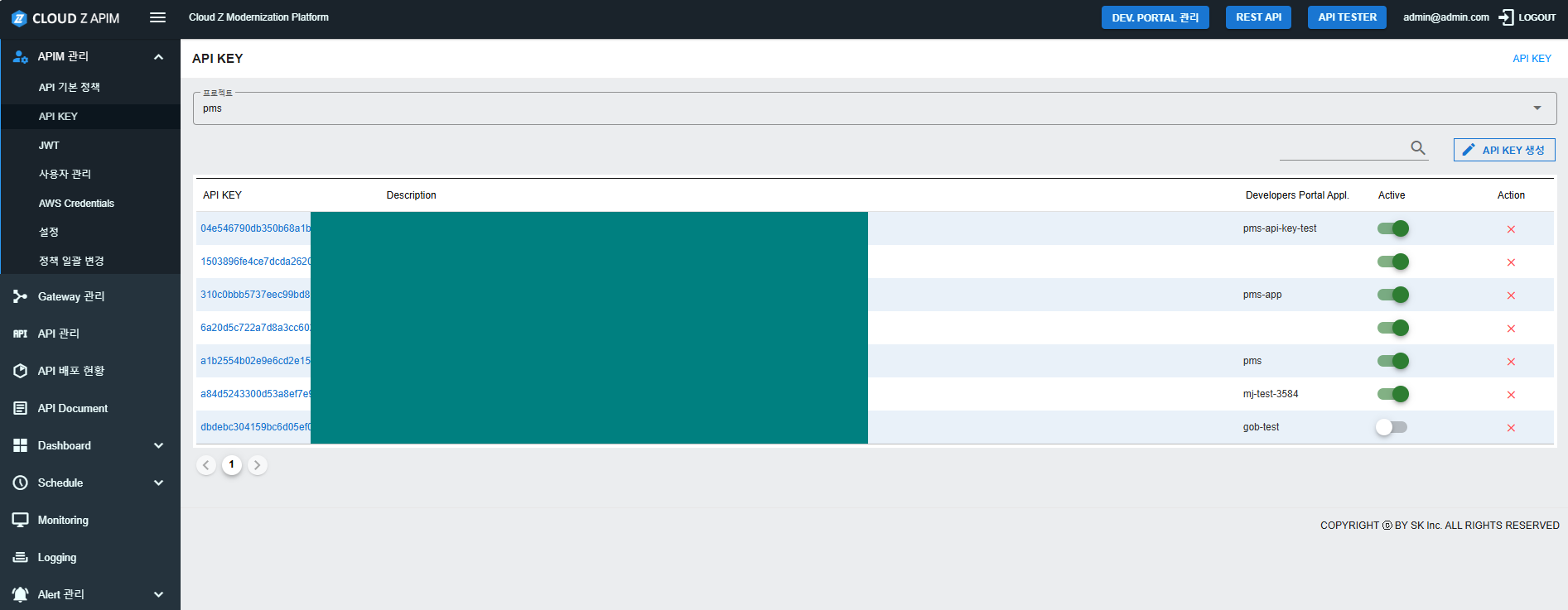
- Once created, the API Key will be displayed in the API Key management screen.
- User can look for the API Key and copy again if needs.
Configuration Fields
The Key Authentication policy includes the following settings:
| Field Name | Description | Data Input |
|---|---|---|
| Header Name | The HTTP header where the API Key should be included in the request. The default header name is x-apim-key. In the Kubernetes deployment 'apim-dff', you can change the header name via environment variables. Modifying these variables will restart the APIM Console and may cause a brief service disruption. | Can be configured via environment variables (K8s only). |
| API Key Validation | The system verifies if the provided API Key is registered and valid before allowing API access. Note: API Keys are typically 32-character alphanumeric strings. | Automatic validation |
| Error Handling | If no valid API Key is provided, the request is rejected with an HTTP 401 Unauthorized response. | Automatic response |
Example API Call with Key Authentication
To make an authenticated API request, include the API Key in the request headers:
GET /api/resource HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
headers: { "x-apim-key": "202cb962ac59075b964b07152d234b70" }
If the API Key is valid, the request is processed successfully. Otherwise, the response will return:
{
"message": "Invalid authentication credentials",
"status": 401
}