OpenID Connect (OIDC)
Overview
The OIDC (OpenID Connect) Policy enables authentication and authorization for APIs by integrating with an OIDC Provider. This ensures that only authenticated users can access the API, either through a token-based approach or an authorization flow.
Configuration Details
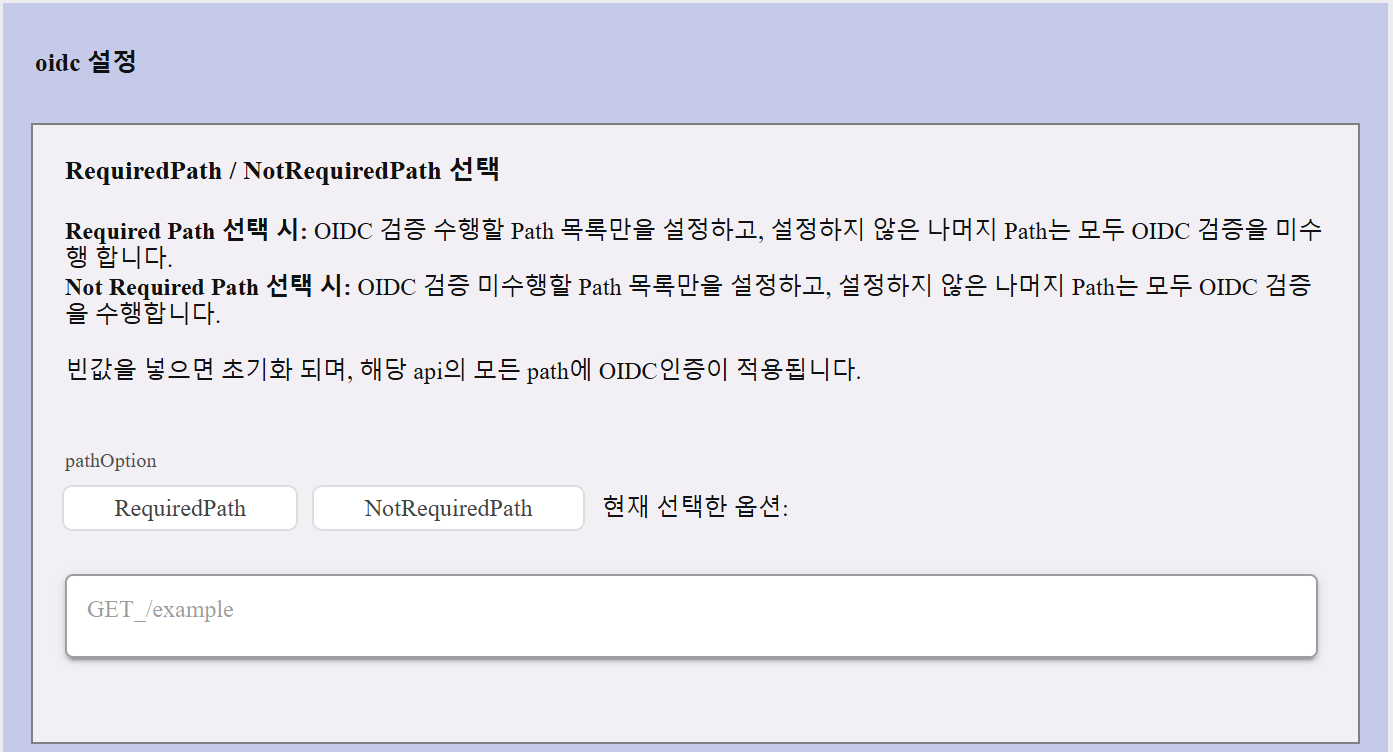
Required Path / Not Required Path
- Required Path: OIDC authentication is enforced only for the listed paths.
- Not Required Path: OIDC authentication is skipped for the listed paths, but enforced for all others.
- If no path is specified, OIDC authentication applies to all paths.
- Switching between path options will require confirmation

Grant Type Configuration
The OIDC policy supports two Grant Types, which determine the authentication flow:
- Authorization Code Grant: Redirects users to the OIDC provider for authentication.
- Password Grant: Directly exchanges user credentials for an ID token.
Each grant type has its own set of configurations:
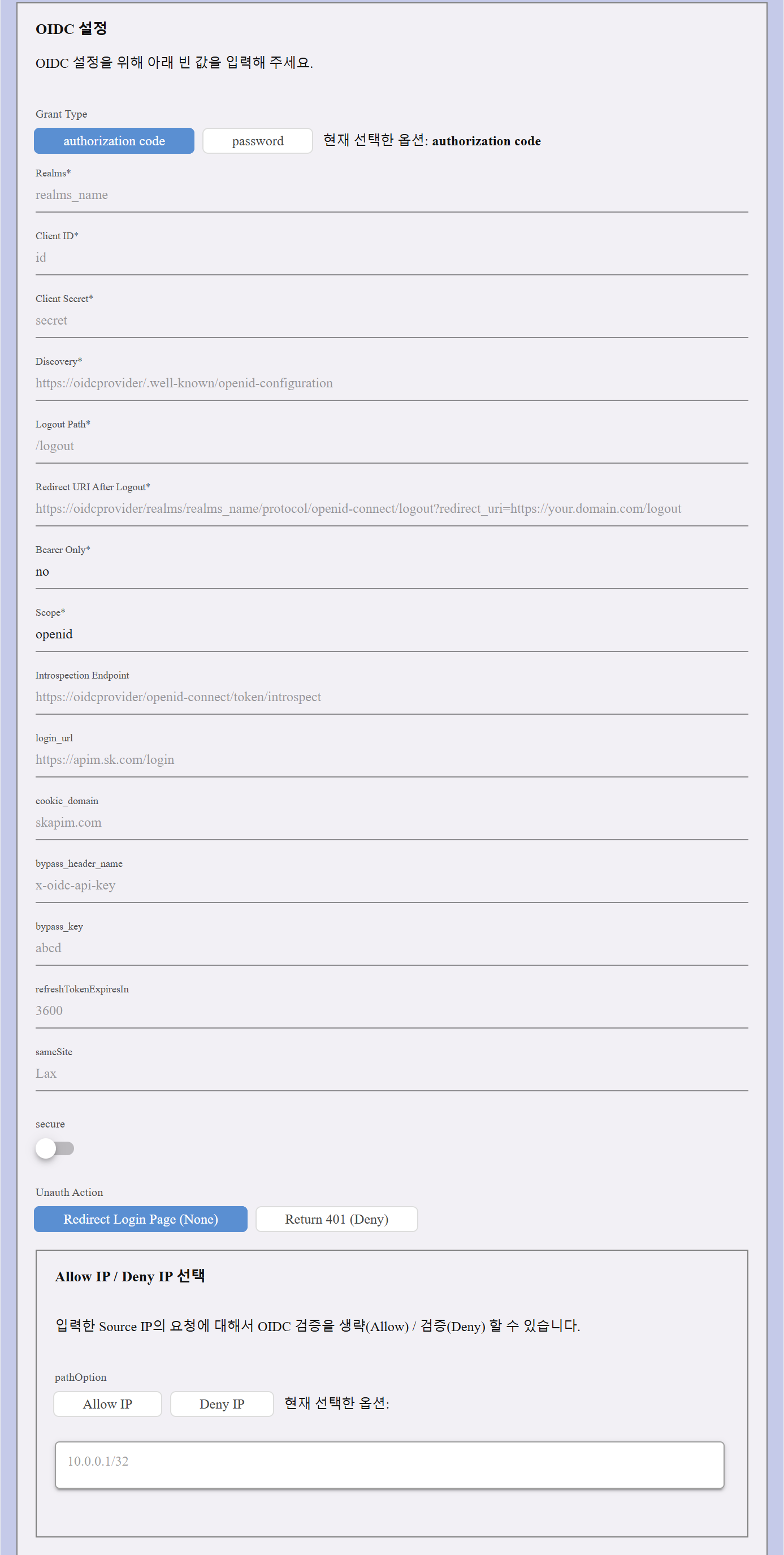
Authorization Code Grant:This flow is primarily used for web applications, where users authenticate via a login page.
| Configuration Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Realm | The name of the authentication realm. Example: realms_name |
| Client ID | The unique identifier assigned by the OIDC provider. |
| Client Secret | The client secret required for authentication. |
| Discovery | The URL to the provider’s discovery endpoint (e.g., https://oidcprovider/.well-known/openid-configuration). |
| Logout Path | The logout endpoint for users (e.g., /logout). |
| Redirect URI After Logout | The redirect URI parameter and value for logout path |
| Bearer Only | Defines if bearer tokens are required: yes (only token authentication) or no (allows both token and login redirection). |
| Scope | Specifies access levels (default: openid). |
| Introspection Endpoint | URL for token validation. |
| Login URL | API endpoint for user login. |
| Cookie Domain | The domain associated with authentication cookies (e.g., skapim.com). |
| Bypass Header Name | Allows skipping authentication for specific requests using a header key (e.g., x-oidc-api-key). |
| Bypass Key | The actual bypass key value. |
| Refresh Token Expiration | Token expiration time (default: 3600 seconds). |
| SameSite | Cookie setting to control cross-site request handling. Options: Lax, Strict, or None. |
| Secure | Enables or disables secure cookies (default: false). |
| Unauth Action | Defines behavior when authentication fails. Options: Redirect to Login Page or Return 401 (Deny). |
| Allow IP / Deny IP | Allows or blocks specific IPs from OIDC authentication. |
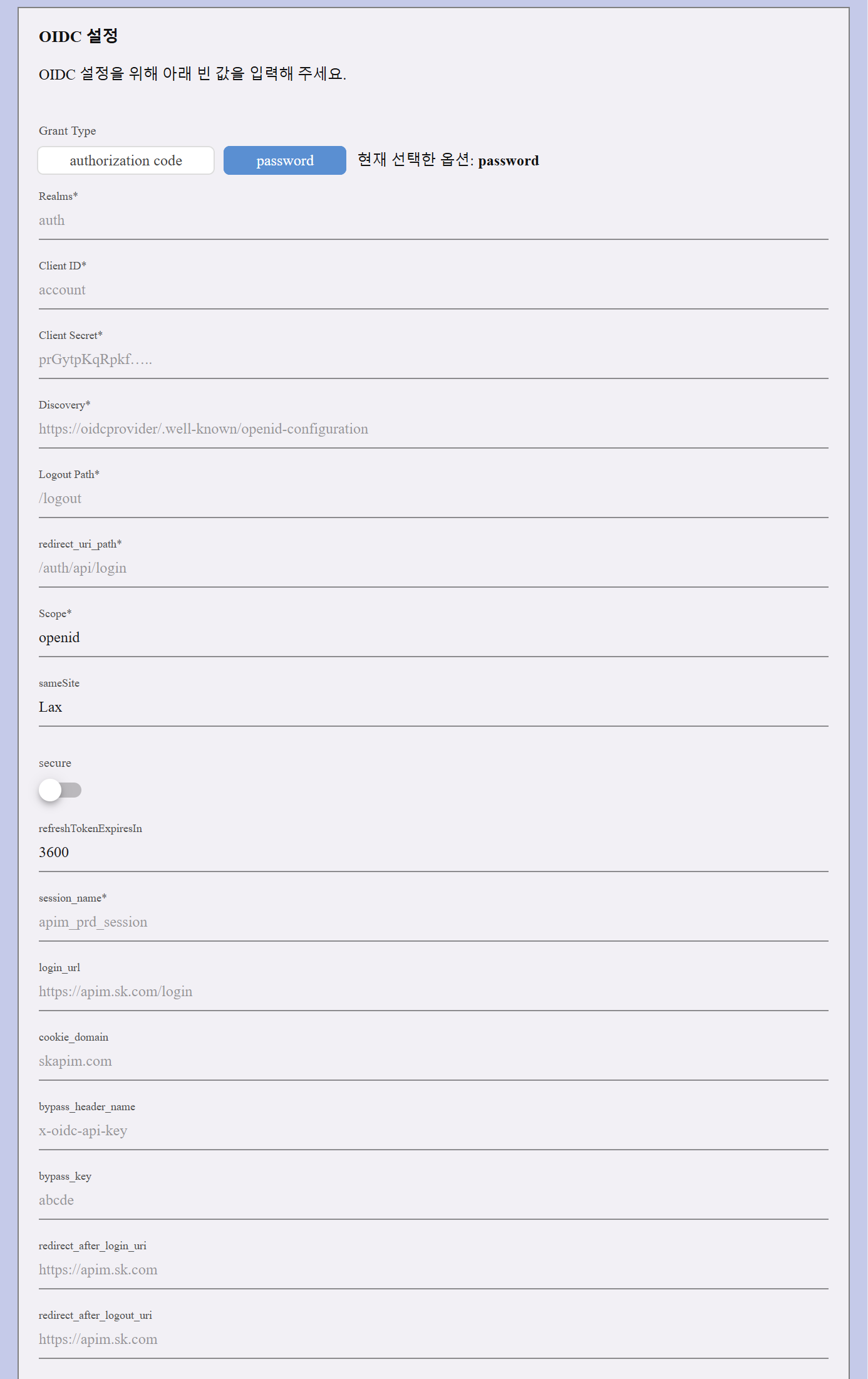
This flow is typically used for machine-to-machine authentication or trusted clients.
| Configuration Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Realm | The name of the authentication realm. Example: auth |
| Client ID | The unique identifier assigned by the OIDC provider (e.g., account). |
| Client Secret | The client secret required for authentication. |
| Discovery | The URL to the provider’s discovery endpoint (e.g., https://oidcprovider/.well-known/openid-configuration). |
| Logout Path | The logout endpoint for users (e.g., /Logout). |
| Redirect URI path | The endpoint for redirecting users after login (e.g., /auth/api/login). |
| Scope | Specifies access levels (default: openid). |
| SameSite | Cookie setting to control cross-site request handling. Options: Lax, Strict, or None. |
| Secure | Toggle to turn on / off secure option |
| Refresh Token Expiration | Token expiration time (default: 3600 seconds). |
| Login URL | API endpoint for user login. |
| Session Name | Defines the session storage name (e.g., apim_prod_session). |
| Cookie Domain | The domain associated with authentication cookies (e.g., skapim.com). |
| Bypass Header Name | Allows skipping authentication for specific requests using a header key (e.g., x-oidc-api-key). |
| Bypass Key | The actual bypass key value. |
| Redirect After Login URI | URL to redirect users after a successful login. |
| Redirect After Logout URI | URL to redirect users after logout. |
Note:
- Authorization Code Grant requires a login page redirection, whereas Password Grant is a direct API request.
- Bearer Only Mode:
- If set to yes, only token-based authentication is allowed.
- If set to no, both login redirection and token authentication are supported.
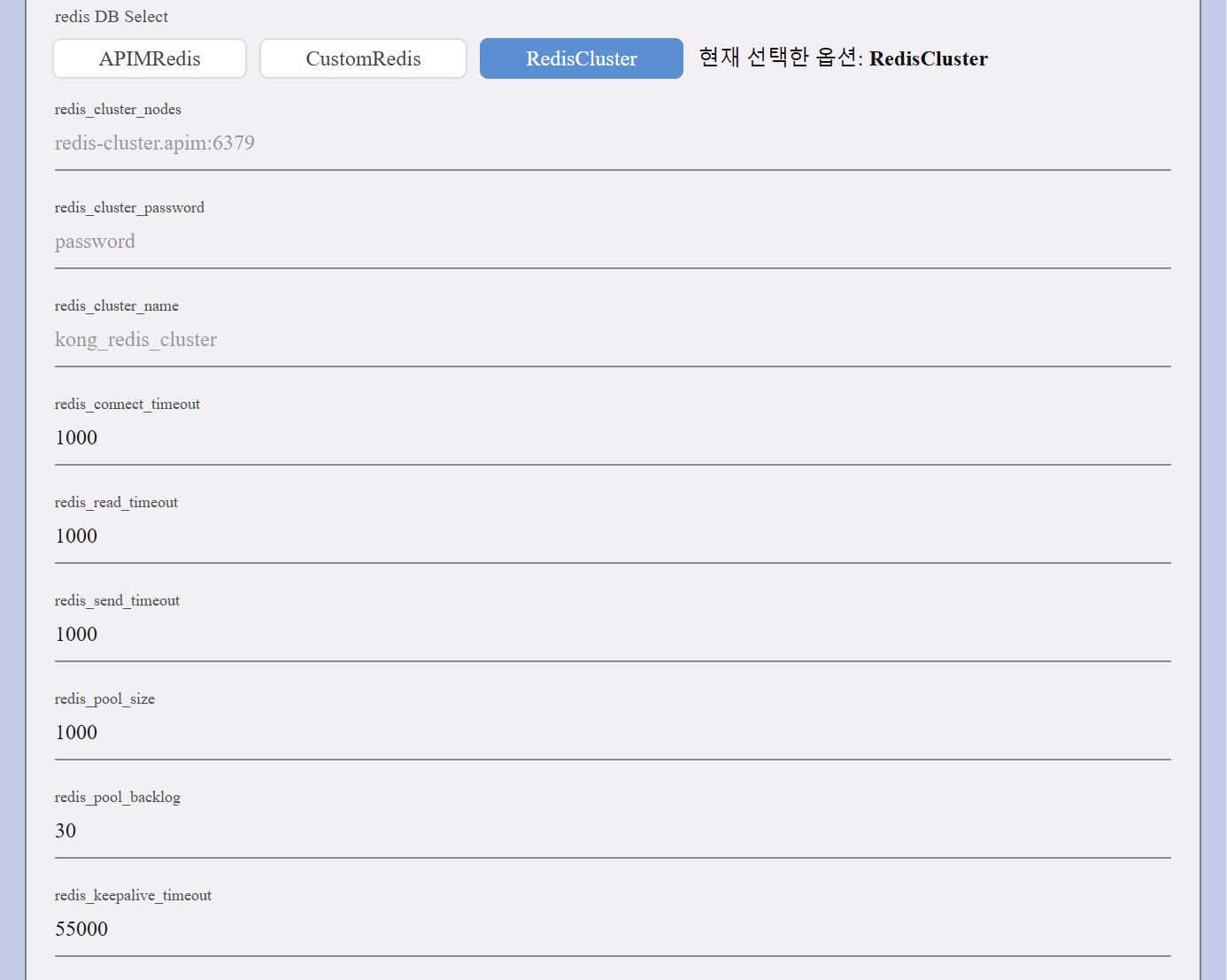
Redis Database Selection
Session data can be stored in different types of Redis databases. The selected Redis type determines which configurations need to be set.
APIM Redis (Default)- Uses the built-in APIM Redis for session storage.
- No additional configuration is required.
- Allows connecting to an external Redis instance.
| Configuration Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Redis Host | Address of the Redis server (e.g., 127.0.0.1). |
| Redis Port | Port number of the Redis server (e.g., 6379). |
| Redis Password | Password for authentication. |
| Redis Database | Specifies which database index to use (e.g., 1). |
| Redis Pool Size | Maximum number of connections in the Redis connection pool (default: 1000). |
| Redis Pool Backlog | Maximum number of requests waiting for an available connection (default: 30). |

- Uses a distributed Redis setup for session storage.
| Configuration Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Redis Cluster Nodes | The cluster node addresses (e.g., redis-cluster.apim:6379). |
| Redis Cluster Password | Password for authentication. |
| Redis Cluster Name | Specifies the cluster name (e.g., kong_redis_cluster). |
| Redis Connect Timeout | Timeout for establishing a Redis connection (default: 1000ms). |
| Redis Read Timeout | Timeout for reading data from Redis (default: 1000ms). |
| Redis Send Timeout | Timeout for sending data to Redis (default: 1000ms). |
| Redis Pool Size | Maximum number of connections in the Redis connection pool (default: 1000). |
| Redis Pool Backlog | Maximum number of pending connections (default: 30). |
| Redis Keepalive Timeout | Maximum idle time before Redis connection is closed (default: 55000ms). |
Additional Notes on OIDC Authentication Behavior
OIDC (OpenID Connect) enables client applications to authenticate users via an external OIDC Provider.
Logout Path and Redirect URI Behavior
When configuring the Logout Path and Redirect URI After Logout, behavior depends on the structure of your API Gateway:
- Suppose your Gateway URL is https://your.domain.com and the Base Path of the API is /basePath.
- If you set Logout Path in the OIDC policy as /logout, then the full logout URL becomes: https://your.domain.com/basePath/logout
- When this URL is called, the logout is handled internally by the OIDC Provider.
- After logout, the browser is redirected to the Redirect URI After Logout (i.e., the redirect_uri value), which must be explicitly defined in the request.
If the full logout URL and redirect_uri are not properly set, the logout process may not redirect as expected.
Two Authentication Methods Supported
OIDC allows two ways to perform authentication:
- Browser-redirected login screen: The browser is redirected to the OIDC login page for user authentication.
- ID token in request: The client sends the ID token directly via HTTP without redirecting the user.
The behavior of these methods depends on the bearerOnly setting:
| bearerOnly Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| no | Both (1) and (2) methods are allowed. |
| yes | Only method (2) is allowed. The system does not redirect to a login page. |
Token Validation and Header Format
- To validate ID tokens using method (2), you must configure the Introspection Endpoint — the endpoint that checks the token validity.
- When calling APIs with an ID token, include the token in the request header using the following format:
Authorization: bearer your_ID_token