Storage Volume Management
The following sections in this guide provides the patterns of cloud-native services (applications) using AMDP. AMDP allows for the configuration of the same cloud-native services in various environments after creating a project and through profiles. Moreover, services can be structured by distinguishing profiles according to bound areas. Each profile manages applications for configuring native services in a Kubernetes environment, BACKING services like databases and message queues required by applications, STORAGE for creating PVCs to connect to existing Kubernetes PVs, and Service Traffic management.
Storage Volume List
This is the interface for managing STORAGE (PVC - Persistent Volume Claim) information to be used by applications.
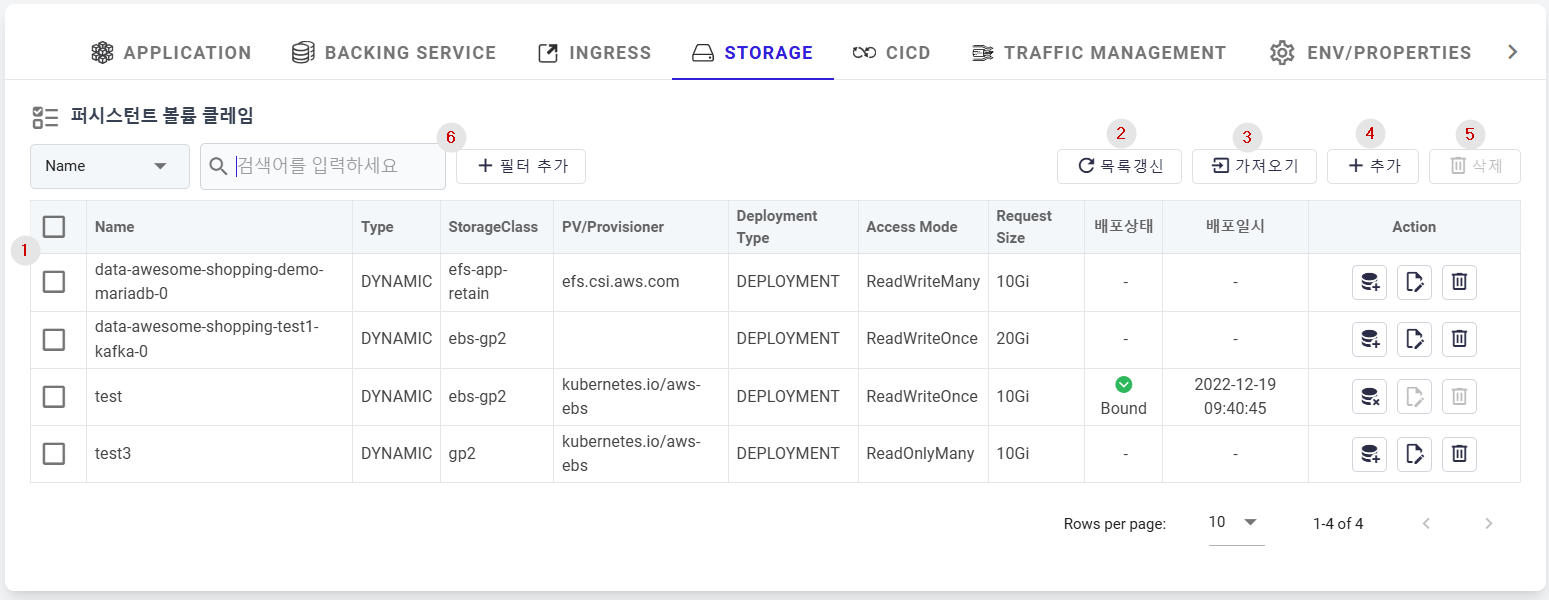
① List of storage (PVC) currently registered in the profile.
- Name: The name of the registered storage.
- Type: Indicates the provisioning type of the storage.
- DYNAMIC: Automatically creates a Persistent Volume using StorageClass information.
- STATIC: Creates a PVC by selecting from already created persistent volumes.
- StorageClass: A class that defines various policies for a volume, such as quality levels and backup policies, allowing dynamic provisioning by automatically creating and allocating volumes.
- PV/Provisioner: Name of the Persistent Volume or provisioner information for the
Persistent Volume.
- PV: The name of the Persistent Volume for STATIC type.
- Provisioner: Provisioner information for DYNAMIC type.
- Deployment Type: The deployment method of the Pod, providing two types: DEPLOYMENT and STATEFULSET.
- Access Mode: ReadWriteMany or ReadWriteOnce.
- ReadWriteMany: The volume can be mounted for read-write by multiple nodes.
- ReadWriteOnce: The volume can be mounted for read-write by one node. Even with ReadWriteOnce access mode, multiple pods can access the volume if they are running on the same node.
- Request Size: Indicates the storage capacity of the PV.
- Deployment Status: Shows the deployment status of the PVC.
- Bound: Indicates that the volume is successfully bound to the claim.
- Pending: Indicates that the binding is waiting for some reason.
- Deployment Date: Shows the date when the PVC was deployed.
- Deploy: You can deploy/delete the registered PVC in the cluster.
- Action: Additional action buttons for storage.
- Edit: Redirects to the storage edit page.
- Delete: Deletes the storage.
② Refresh List: Refresh and displays the storage (PVC) list.
③ Import: You can select and register from PVCs deployed in the Kubernetes cluster.
④ Add: Button to add new storage (PVC).
⑤ Delete: Delete the selected PVCs in the list in bulk.
⑥ Filter the storage list by Name, Type, Deployment Type or Access Mode value input in the search field.
Importing Storage/PVC
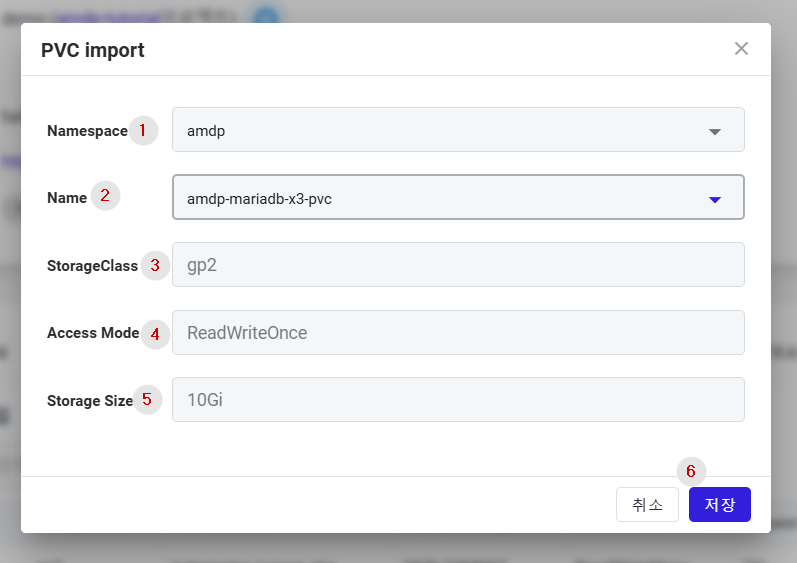
① Namespace: Select the cluster namespace where the PVC is deployed.
② Name: Displays the list of storages (PVCs) deployed in the selected namespace, from which you select the storage to import.
③ Storage Class: Displays the storage class name of the selected PVC in a read-only format.
④ Access Mode: Displays the access mode information of the selected storage in a read-only format.
⑤ Storage Size: Displays the storage capacity information of the selected storage in a read-only format.
⑥ Register the selected storage information.
Adding Storage/PVC (Dynamic Provisioning)
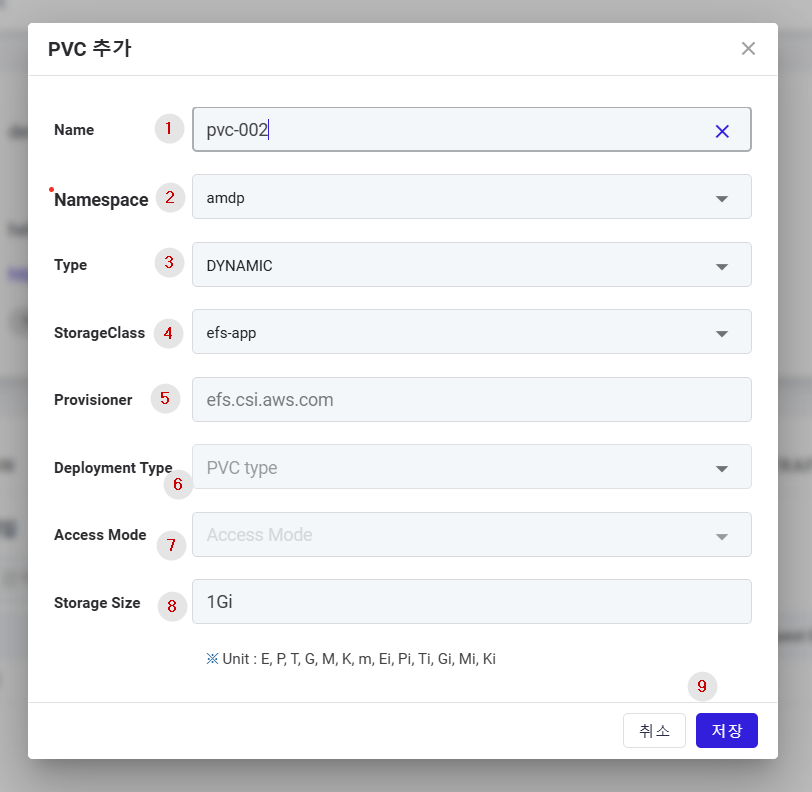
① Name: Enter the name of the storage (PVC).
② Namespace: Enter the cluster namespace where the storage will be deployed.
③ Type: Enter the type of persistent volume provisioning. In this case Type must be DYNAMIC
④ Storage Class: A class defining various policies for a volume, used only when the provisioning type is DYNAMIC.
⑤ Provisioner: If the type is Dynamic, select the provisioner information for the PV.
⑥ Deployment type: Choose between DEPLOYMENT/STATEFULSET.
⑦ Access Mode: Automatically selected between ReadWriteMany / ReadWriteOnce depending on the Deployment Type.
⑧ Storage Size: Enter the storage capacity in the standard unit defined below.
⑨ Save Button: Click to save the storage.
Adding Storage/PVC (Static Provisioning)
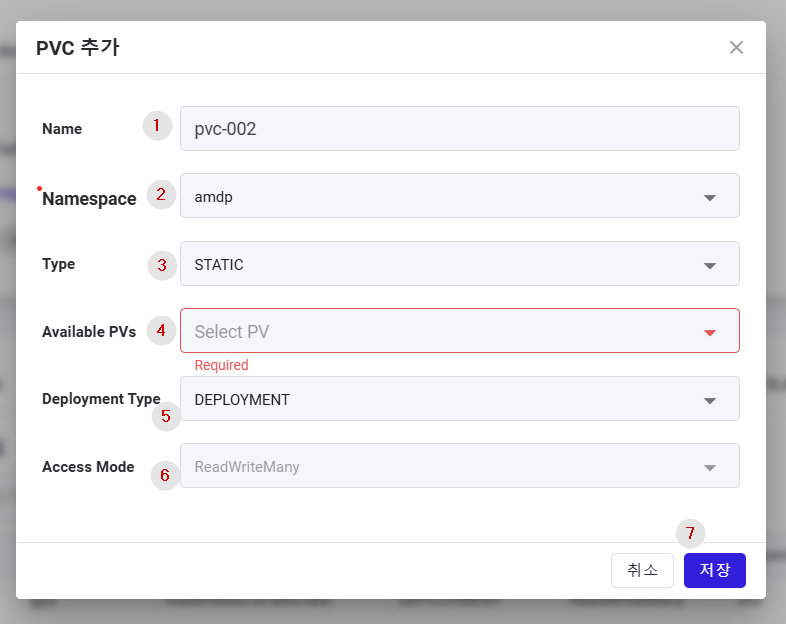
① Name: Enter the name of the storage (PVC).
② Namespace: Enter the cluster namespace where the storage will be deployed.
③ Type: Enter the type of persistent volume provisioning. In this case Type must be STATIC
④ Available PVs: Unlike Dynamic, Static provisioning involves selecting an available PV from the deployed PVs to create it.
⑤ Deployment Type: Choose between DEPLOYMENT/STATEFULSET.
⑥ Access Mode: Automatically selected between ReadWriteMany/ReadWriteOnce depending on the Deployment Type
⑦ Save button: Click to store the new storage.
Editing Storage/PVC
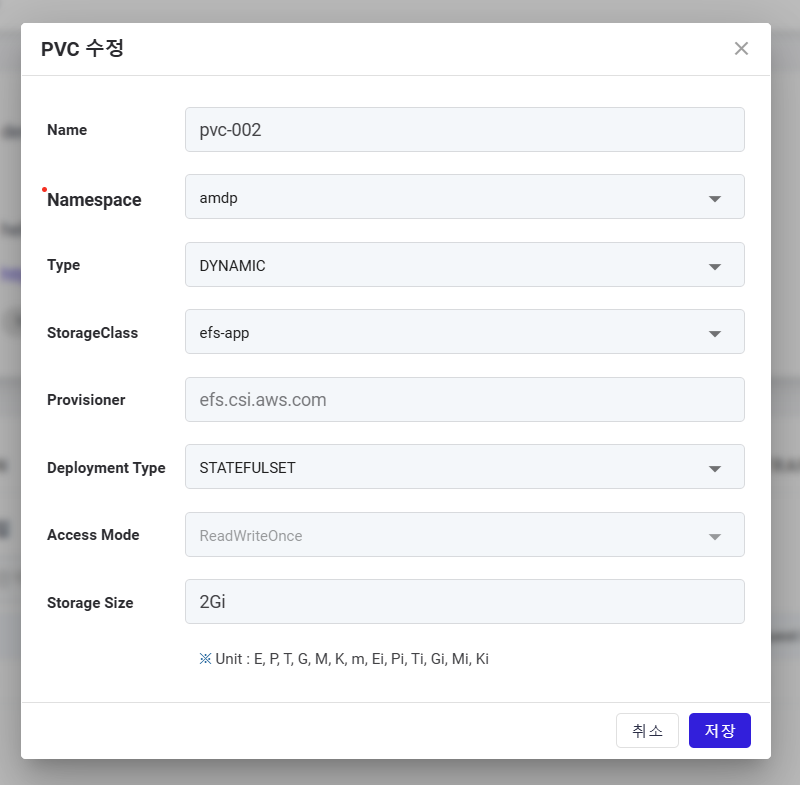
This is the screen for editing a registered storage (PVC). The items are the same as the add screen.
- Save: To save the modified storage information.
- Cancel: To not save the modified storage information and close the popup.