Dependency Management
Cloud ZCP utilizes Sonatype Nexus as its integrated repository management tool for handling application dependencies. Nexus plays a crucial role in managing software binaries required by applications, such as Java libraries (JARs), Node modules, and potentially other artifact types.
Its key functions include:
- Proxying Public Repositories: Nexus can act as a local proxy (or mirror) for public repositories like Maven Central, npmjs.org, etc. This allows development and build environments, especially those in closed networks, to access external dependencies reliably and efficiently by caching downloaded artifacts.
- Hosting Internal Libraries: Nexus provides
hostedrepositories where organizations can upload and manage their own internal libraries or shared components. - Grouping Repositories: Repositories can be grouped together, allowing build tools to search across multiple sources (e.g., first checking a hosted repository for internal libraries, then checking a proxy repository for external ones).
Access Nexus
You can access the Nexus interface through the project menu in the ZCP console: Dev Tools > Nexus.
Standard project users typically do not have accounts to log into the Nexus UI directly. Viewing repositories is possible through the Browse menu. Operations like creating hosted repositories or uploading custom libraries usually require assistance from the platform administrator.
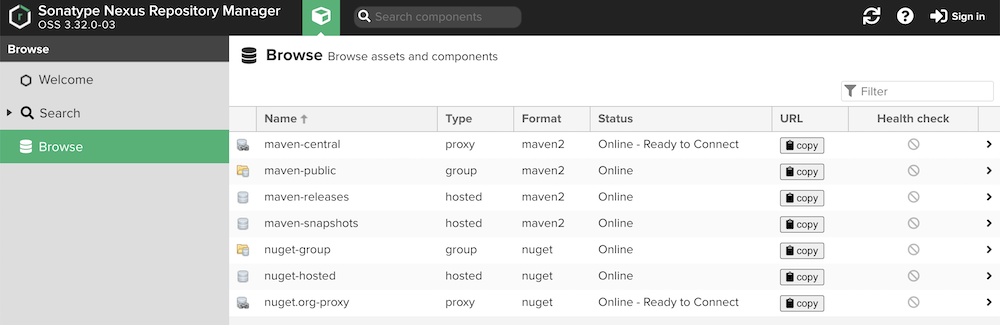
When Browse Nexus, you will encounter different repository types:
- proxy: Mirrors an external public repository. Caches downloaded artifacts.
- hosted: Stores internally developed or uploaded artifacts.
- group: Combines multiple proxy and/or hosted repositories into a single access point. Libraries are searched for in the defined order within the group.
Use Nexus as a Maven Mirror
For Java projects using Maven, especially in environments without direct internet access, Nexus can be configured as a mirror repository.
- Configuration File: Modify Maven's
settings.xmlfile (usually located in~/.m2/settings.xmlor/conf/settings.xmlwithin the Maven installation). - Mirror Settings: Add a
<mirror>entry within the<mirrors>section:
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
...
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>modernizationplatform</id> <name>Modernization Platform Nexus</name> <url>NEXUS_REPOSITORY_URL</url> <mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf> </mirror>
</mirrors>
...
</settings>
- Finding the URL: In the Nexus UI (Browse section), locate the desired repository (typically a
grouptype repository that includes proxies for public repos and potentially internal hosted repos) and use theCopy URLbutton to get the correctNEXUS_REPOSITORY_URL. mirrorOfSetting:- Using
*will cause Maven to route all repository requests through this Nexus mirror. - Alternatively, you can specify specific repository IDs (e.g.,
central) if you only want to mirror certain repositories defined in yourpom.xml.
- Using
- IDE Integration: Ensure your development environment (Eclipse, IntelliJ, VSCode, etc.) is configured to use this
settings.xmlfile.
Using Nexus as a Gradle Proxy
For projects using Gradle, you configure Nexus access within the project's build.gradle file.
- Configuration File: Modify the
build.gradle(orbuild.gradle.kts) file for your project. - Repository Settings: Adjust the
repositories { ... }block:
repositories {
// Comment out or remove mavenCentral() or jcenter() if you want to force proxying
// mavenCentral()
maven {
url "NEXUS_REPOSITORY_URL" // URL of the Nexus *group* repository
}
}
- Finding the URL: As with Maven, find the appropriate
grouprepository URL in the Nexus UI using theCopy URLbutton. By replacingmavenCentral()with the Nexusmavenblock, you direct Gradle to resolve dependencies through Nexus.
Manage Custom Libraries (Hosted Repositories)
hosted repositories in Nexus are designed to store artifacts that are not available in public repositories, such as internally developed libraries or specific versions of third-party libraries.
Build tools can access these internal libraries when the hosted repository is included in a group repository that is configured in the build (settings.xml or build.gradle).
Uploading artifacts to hosted repositories typically requires administrative privileges within Nexus. Project teams usually need to coordinate with platform administrators for this purpose.