API Gateway Creation
Overview
Creating an API Gateway is the first step to exposing and managing APIs through the APIM system. In real production environments like APIM’s infrastructure, the Gateway setup must consider scaling, traffic distribution, log forwarding, and DNS mapping. This tutorial guides you through creating a production-grade gateway configured by an example case.
Prerequisites
Ensure the following before you begin:
- You have Administrator access to the APIM Console.
- A Project has been created (e.g., pj-test-01).
Step-by-Step Tutorial
Step 1. Access the Gateway Creation Page
- Log into the APIM Console.
- Select project: pj-test-01.
- Navigate to Gateway Management.
- Click the Create Gateway button.
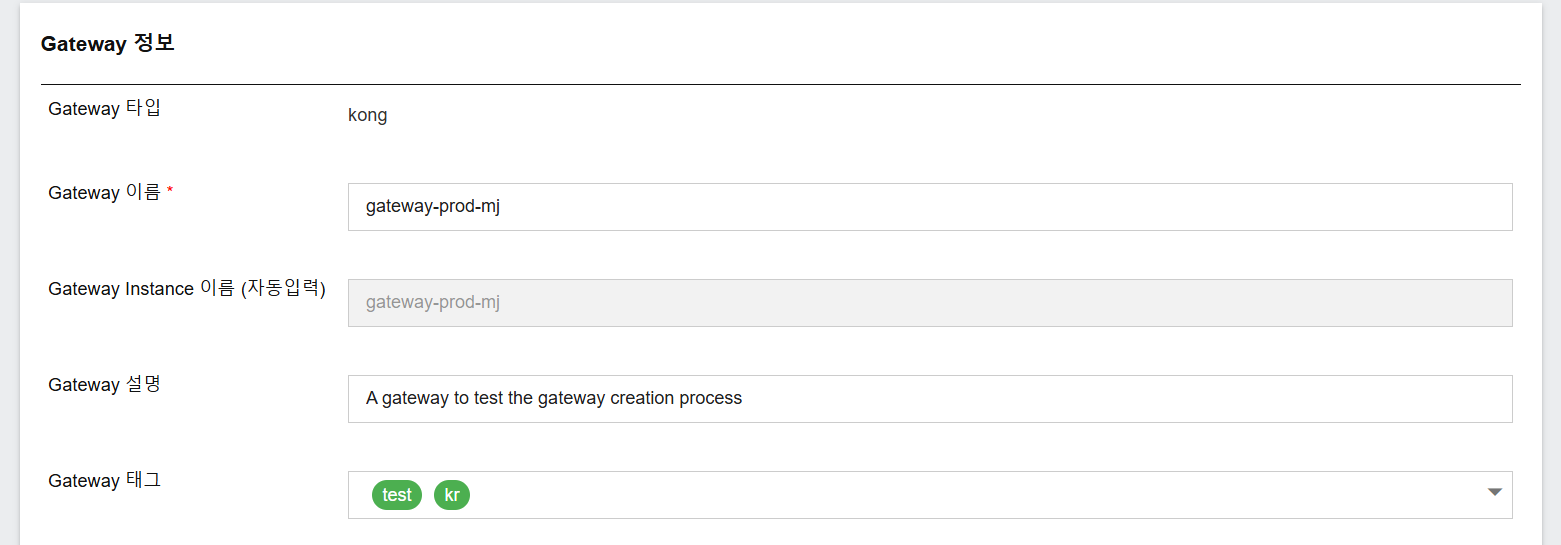
Step 2. Gateway Information
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Gateway Type | kong |
| Gateway Name | gateway-prod-mj |
| Gateway Instance Name | Auto-filled as gateway-prod-mj |
| Description | A gateway to test the gateway creation process |
| Tags | test, kr (can add more tags to categorize gateway) |
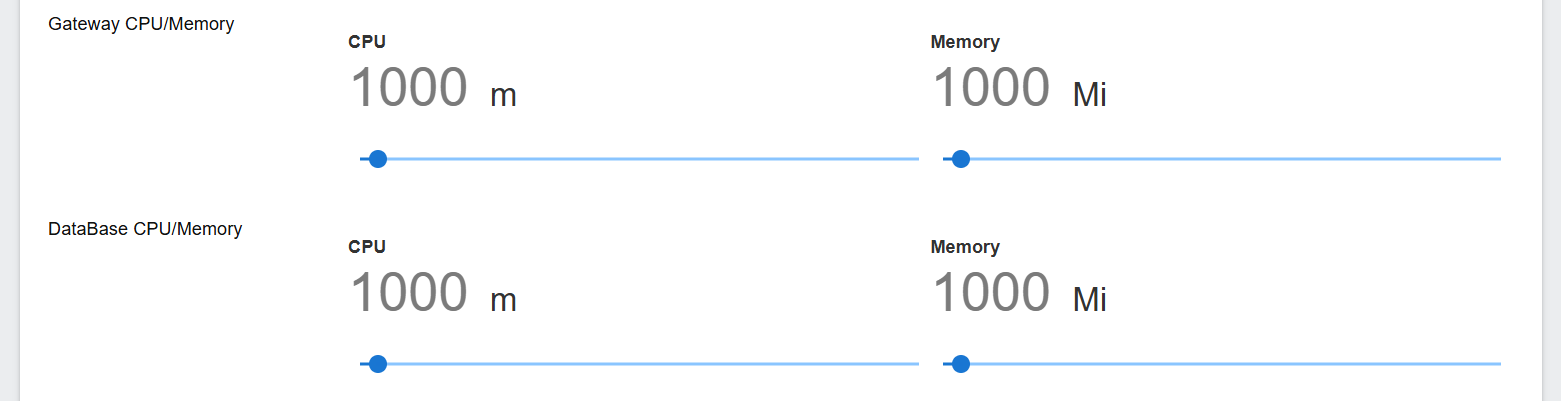
Step 3. Resource Configuration
Gateway Pod Resource
| Resource | Value |
|---|---|
| CPU | 1000m |
| Memory | 1000Mi |
Database Resource
| Resource | Value |
|---|---|
| CPU | 1000m |
| Memory | 1000Mi |
Use the slider to change the values
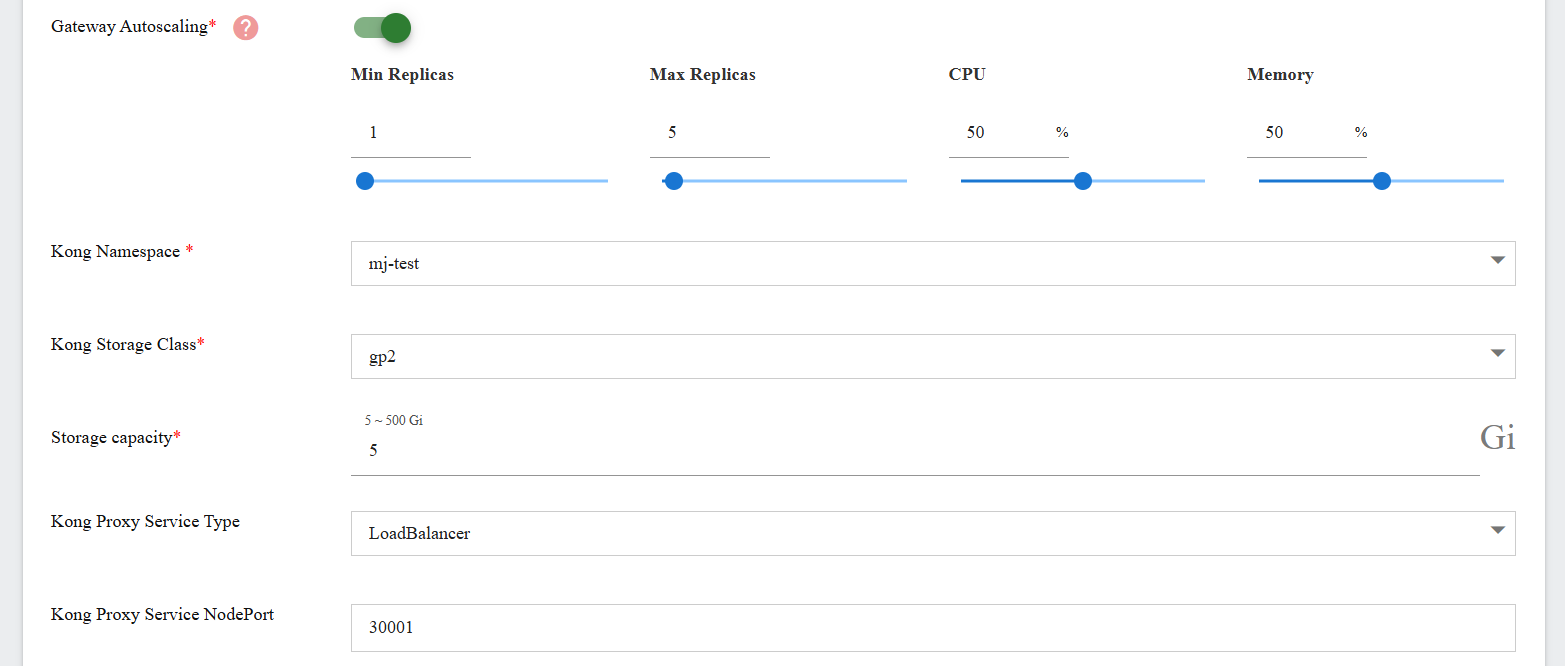
Step 4. Deployment Settings
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Gateway Autoscaling | Enabled (toggle on) Min Replicas: 1 Max Replicas: 5 CPU: 50 Memory: 50 Can input or use slider to change the value |
| Kong Namespace | mj-test |
| Kong Storage Class | gp2 |
| Storage Capacity | 5 Gi |
| Kong Proxy Service Type | LoadBalancer |
| Kong Proxy Service NodePort | 30001 |
Step 5. Affinity Settings
Enable Affinity and configure:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| topology.kubernetes.io/zone | ap-northeast-2 |
This ensures gateway pods are scheduled only in specific availability zones.

Step 6. Toleration Settings
Enable Toleration and add:
| Operator | Key | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Equal | spot | true |
| Exists | critical |
This allows gateway pods to be scheduled onto nodes with taints such as spot=true or critical.

Step 7. Topology Spread Configuration
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Max Skew | 1 |
| When Unsatisfiable | DoNotSchedule |
Ensures gateway pods are evenly spread across zones and avoids unsatisfiable scheduling.

Step 8. System Add-ons
| Component | Setting |
|---|---|
| Inner Redis | Enabled |
| Fluent Bit | Enabled OpenTelemetry: Enabled Elasticsearch: Disabled |
Enabling Fluent Bit helps centralize gateway logs in your observability pipeline.

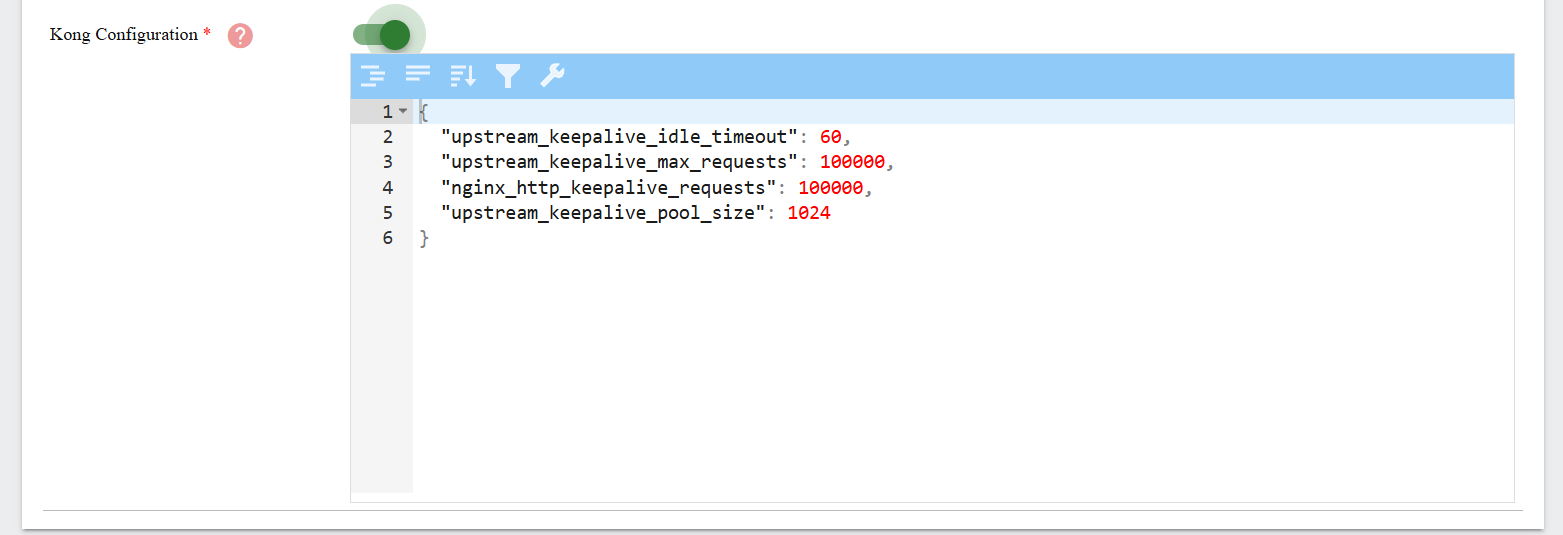
Step 9. Kong Configuration
Enter the following JSON:
{
"upstream_keepalive_idle_timeout": 60,
"upstream_keepalive_max_requests": 100000,
"nginx_http_keepalive_requests": 100000,
"upstream_keepalive_pool_size": 1024
}
These values optimize upstream connection reuse and help in high-performance environments.
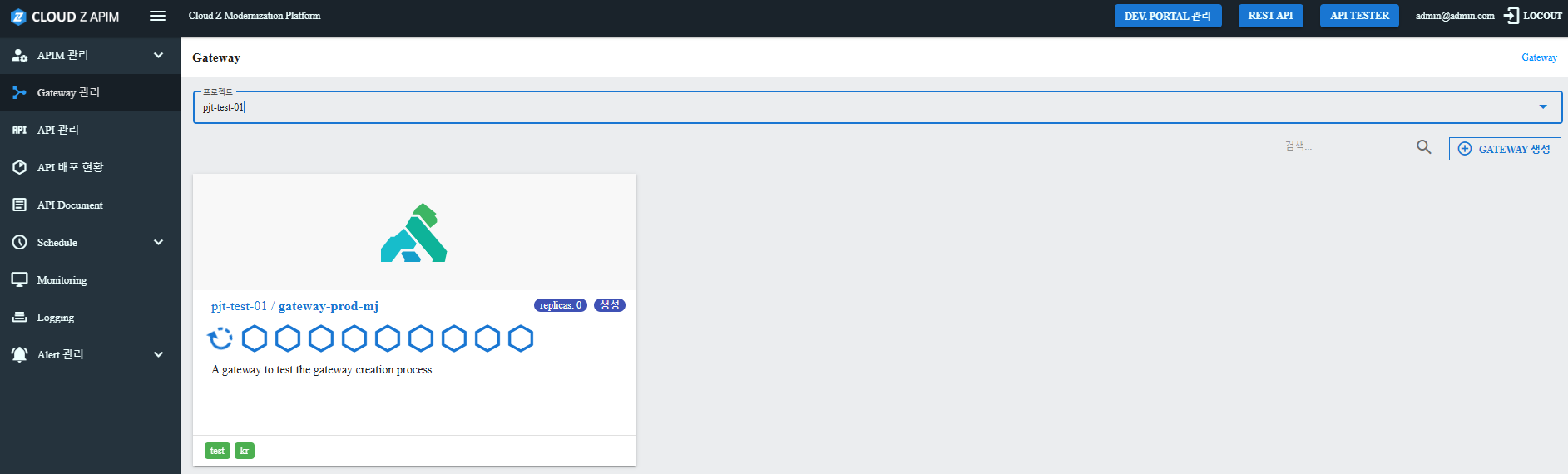
Step 10. Create the Gateway
- Click the Create Gateway button at the bottom.
- Go to the gateway detail page and verify the gateway created.
Best Practices
- Use environmental suffixes in names: gateway-dev, gateway-staging, gateway-prod.
- Define dedicated namespaces per environment for clean resource separation.
- Keep Autoscaling off unless you have metrics-based triggers.
- Use Affinity and Topology Spread together to achieve high availability.
- Document and version your Kong Configuration JSON for audit and rollback.